Management and Treatment of Gynecomastia with Liposuction
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.14228/jpr.v1i4.79Abstract
Background: Gynecomastia is a common problem of the male breast, with a reported overall incidence of 32 to 36 percent. The surgical management of gynecomastia has undergone significant changes over the past few decades, from a predominantly open approach to one involving liposuction only or liposuction combined with direct excision through a periareolar or remote incision.
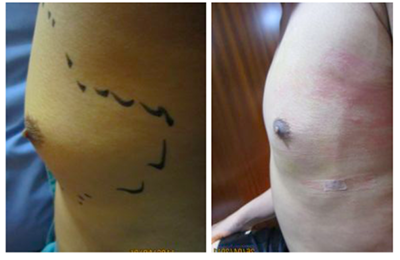
Patients and Method: We present five cases with bilateral gynecomastia. One patient is a teenager and others are adult males. Liposuction only was performed in patients without palpable glandular breast mass. Direct excision was made to help remove the excessive glandular breast mass. The compressive garment is worn for 4 to 6 weeks after procedure to prevent the complications of the surgical procedure.
Result: Three of the patients are corrected with liposuction only. There are two patients who underwent combination of open excision and liposuction. The liposuction procedure only left minimal scar from canulas incision. Other patient has minimal periareolar incision to remove excess breast tissue. None of the patients showed complication after surgery.
Summary: All of the patients presented were satisfied by the correction of gynecomastia using liposuction. None of the patients shows any complication after liposuction procedure. The result after surgery is a natural-looking chest without extensive scar. The patients appreciate the early return to work and normal physical activities.
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
Authors retain the copyright of the article and grant Jurnal Plastik Rekonstruksi the right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License. Articles opting for open access will be immediately available and permanently free for everyone to read, download and share from the time of publication. All open access articles are published under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-Non-commercial-NoDerivatives (CC BY-NC-ND) which allows readers to disseminate and reuse the article, as well as share and reuse of the scientific material. It does not permit commercial exploitation or the creation of derivative works without specific permission.













