The Effectiveness of Intradermal Suture Technique on Hypertrophic Scar Prevention in Rats
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.14228/jprjournal.v9i1.335Keywords:
Fibroblasts, Fibrocytes, Hypertrophic Scars, Intradermal Sutures, PolypropyleneAbstract
Introduction : Hypertrophic scarring is a complication that occurs in post-surgical wounds. There are many ways to prevent scarring, but there have been no satisfactory methods yet. Moreover, no studies investigated the effectiveness of intradermal sutures. Polypropylene thread can be used to repair a scar after surgery. This study aimed to prove the effectiveness of intradermal sutures using polypropylene thread on surgical scar quality.
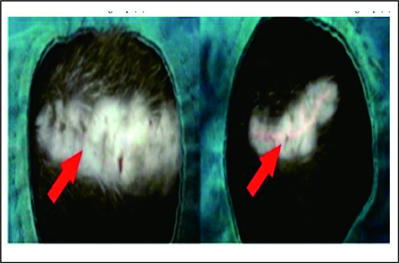
Method : The study was conducted using a randomized, controlled trial, and post-test only with 20 rats (Rattus norvegicus) as animal subjects. The wounds were made on the back, approximately 6 mm x 2 cm. Then, the rats were divided into two groups: a control group without intradermal sutures (K) and treatment group with intradermal sutures (I). Histopathological examination using Hematoxylin and Eosin (H&E) staining was used to identify the fibroblast number on the 21st day. The fibrocytes number were also observed on the 12th week and the Vancouver Scar Scale (VSS) was used to assess the scar quality.
Result : The number of fibroblasts and fibrocytes in the control group (K) was significantly smaller (53.60 ± 14.571; 3.20 ± 0.447) than the treatment (I) (243.20 ± 75.334; 171.40 ± 13.221). The VSS value was significantly greater in the control than the treatment.
Conclusion: The intradermal sutures using polypropylene thread produced a better-quality scar after surgery compared to wounds without intradermal sutures.
References
Perdanakusuma DS. The effect of melanin concentration on collagen accumulation. Folia Med Indo. 2006;42:218-27.
Gauglitz GG, Korting HC, Pavicic T, Ruzicka T, Jeschke MG. Hypertrophic scarring and keloids: pathomechanisms and current and emerging treatment strategies. Mol Med. 2011;17:113-25.
Erickson JR, Echeverri K. Learning from regeneration research organisms: The circuitous road to scar free wound healing. Dev Biol. 2018;433:144-54.
Son D, Harijan A. Overview of surgical scar prevention and management. J Korean Med Sci. 2014;29(6) 751-7.
Atiyeh BS, El Khatib AM, Dibo SA. Pressure garment therapy (PGT) of burn scars: evidence-based efficacy. Ann Burns Fire Disasters. 2013;26:205-12.
Mari W, Alsabri SG, Tabal N, Younes S, Sherif A, Simman R. Novel Insights on Understanding of Keloid Scar: Article Review. J Am Coll Clin Wound Spec. 2016;7:1-7.
Huang C, Murphy GF, Akaishi S, Ogawa R. Keloids and hypertrophic scars: update and future directions. Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open. 2013;1:e25.
Rabello FB, Souza CD, Farina Júnior JA. Update on hypertrophic scar treatment. Clinics (Sao Paulo). 2014;69:565-73.
Ogawa R, Akaishi S. Endothelial dysfunction may play a key role in keloid and hypertrophic scar pathogenesis - Keloids and hypertrophic scars may be vascular disorders. Med Hypotheses. 2016;96:51-60.
Ogawa R. Surgery for scar revision and reduction: from primary closure to flap surgery. Burns Trauma. 2019;7:1-8.
Yang J, Kim KH, Song YJ, Kim SC, Sung N, Kim H, et al. Cosmetic outcomes of cesarean section scar; subcuticular suture versus intradermal buried suture. Obstet Gynecol Sci. 2018;61:79-87.
Elsharkawy SS, Dawood WA. Removed versus unremoved vicryl sutures used for subcuticular skin closure. Int J Reprod Contracept Obstet Gynecol. 2018;7:4877-4881.
Gauglitz GG. Management of keloids and hypertrophic scars: current and emerging options. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2013;6:103-14.
Ireton JE, Unger JG, Rohrich RJ. The role of wound healing and its everyday application in plastic surgery: a practical perspective and systematic review. Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open. 2013;1:e10-9.
Charan J, Biswas T. How to calculate sample size for different study designs in medical research? Indian J Psychol Med. 2013;35:121-6.
Rong X, Chu W, Zhang H, Wang Y, Qi X, Zhang G, et al. Antler stem cell-conditioned medium stimulates regenerative wound healing in rats. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019;10:326.
Kudur MH, Pai SB, Sripathi H, Prabhu S. Sutures and suturing techniques in skin closure. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2009;75 425-34.
Hong WX, Hu MS, Esquivel M, Liang GY, Rennert RC, McArdle A, et al. The role of hypoxia-inducible factor in wound healing. Adv Wound Care (New Rochelle). 2014;3:390-9.
Ruthenborg RJ, Ban JJ, Wazir A, Takeda N, Kim JW. Regulation of wound healing and fibrosis by hypoxia and hypoxia-inducible factor-1. Mol Cells. 2014;37:637-43.
Bishop A. Role of oxygen in wound healing. J Wound Care. 2008;17:399-402.
Aoki M, Akaishi S, Nakao J, Dohi T, Hyakusoku H, Ogawa R. Objective spectrometric measurement of keloid color in the East Asian population: Pitfalls of subjective color measurements. J Nippon Med Sch. 2016;83:142-9.
Timmenga EJ, Andreassen TT, Houthoff HJ, Klopper PJ. The effect of mechanical stress on healing skin wounds: an experimental study in rabbits using tissue expansion. Br J Plast Surg. 1991;44:514-9.
Gu Y, Ampofo E, Menger MD, Laschke MW. miR-191 suppresses angiogenesis by activation of NF-κB signaling. FASEB J. 2017;31:3321-33.
Aurora AB, Biyashev D, Mirochnik Y, Zaichuk TA, Sánchez-Martinez C, Renault MA, et al. NF-kappaB balances vascular regression and angiogenesis via chromatin remodeling and NFAT displacement. Blood. 2010;116:475-84.
Andrews JP, Marttala J, Macarak E, Rosenbloom J, Uitto J. Keloids: The paradigm of skin fibrosis - Pathomechanisms and treatment. Matrix Biol. 2016;51:37-46.
Landén NX, Li D, Ståhle M. Transition from inflammation to proliferation: a critical step during wound healing. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2016;73:3861-85.
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2022 Herman Yosef Limpat Wihastyoko, Wicaksono Patria Wuryanjono

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
Authors retain the copyright of the article and grant Jurnal Plastik Rekonstruksi the right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License. Articles opting for open access will be immediately available and permanently free for everyone to read, download and share from the time of publication. All open access articles are published under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-Non-commercial-NoDerivatives (CC BY-NC-ND) which allows readers to disseminate and reuse the article, as well as share and reuse of the scientific material. It does not permit commercial exploitation or the creation of derivative works without specific permission.













