Sole Reconstruction Using Anterolateral Thigh Free Flap: A Review of 4 Cases
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.14228/jpr.v2i3.165Abstract
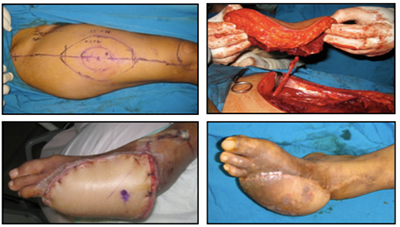
Background: The ideal technique for sole reconstruction should meet such requisite as a durable and comfortable weight-bearing surface, solid anchoring to deep tissue for resistance to shear force and adequate protective sensation. The anterolateral thigh (ALT) perforator free flap provides a large, pliable skin island and sufficient bulk, allowing three-dimensional tailoring to complex defects. The present article is about our experience of sole reconstruction ALT perforator free flap.
Patient and Method: Total of 4 flaps in the foot defects was performed in February 2009 to December 2012. We reconstructed soft tissue defects in the sole using ALT free flaps, the complications, aesthetic and function results were monitored.
Result: ALT perforator free flap provided stable and durable long-term wound cover in all patients, resulting in early rehabilitation and function outcomes were completely achieved. Complications were few
and manageable in all cases.
Summary: ALT perforator free flap has become common procedure in many centers around the world. The numerous advantages include stable wound coverage; improve aesthetic and functional outcomes,
and minimal donor site morbidity. In our experiences, we found that the use of ALT perforator free flap in sole defect reconstruction, to be technically affordable, reliable and have resulted in excellent outcomes.
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
Authors retain the copyright of the article and grant Jurnal Plastik Rekonstruksi the right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License. Articles opting for open access will be immediately available and permanently free for everyone to read, download and share from the time of publication. All open access articles are published under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-Non-commercial-NoDerivatives (CC BY-NC-ND) which allows readers to disseminate and reuse the article, as well as share and reuse of the scientific material. It does not permit commercial exploitation or the creation of derivative works without specific permission.













